Review Article
Year: 2022 |Volume: 1 | Issue: 03 |Pages: 134-145
Role of Jambeer Pinda Sweda in Gridhrasi w.s.r. to Sciatica
About Author
Correspondence Address:
Corresponding author : Dr. Prasanna Rajenda Pawar. PG Scholar, Department of Panchakarma, CSMSS Ayurveda Mahavidyalaya, Kanchanwadi, Aurangabad, 431002, dr.prasannapawar@gmail.com
Date of Acceptance: 2022-09-30
Date of Publication:2022-10-16
Article-ID:AYU_26_10_22 https://ayuscript.com
Source of Support: Nill
Conflict of Interest: Nill
How To Cite This Article: : Pawar PR, Neralkar UK, Role of Jambeer Pinda Sweda in Gridhrasi w.s.r. to Sciatica. AYUSCRIPT 2022;1(3):134-145
Abstract
In ayurveda, one of the most common diseases that affect the hip and the lower limbs is gridhrasi. Gridhrasi is one of the severe debilitating disorder amongst all the neurological disorders. The main symptoms of Gridhrasi are Ruka (pain), Toda (pricking sensation), Stambha (stiffness) and Muhuspandana (twitching) in the Sphika (Gluteal Region), Kati (Low Back), Uru (Thigh), Janu (Knee), Jangha (Calf) and Pada (Foot) respectively and Sakthikshepa Nigraha (restricted lifting of the leg). These symptoms can be compared with sciatica which is characterised by severe pain starting from low back region and radiating down towards the foot. Though many conventional treatments are available but in view of their side effects and dependency it is important to search for safe and effective ayurvedic treatments. Ayurveda treats it by snehan, swedana, shodhana, and shaman chikitsa which are simple, safe and cost effective. The prevalence of sciatica symptoms increasing,Sciatica is more common among the age group between 30-50 years of age.Pinda sweda is a type of sankar sweda explained in the ayurvedic classics, is more effective for the shaman of vitiated vata dosha in the above condition. Drugs used in jambeer pinda sweda has vata kaphahara, shothahara, shulaghana action. This paper is review of clinical application of Jambeer pinda Sweda and its efficacy in Gridrasi.
Keywords - Gridhrasi, Sciatica, Pinda sweda
Introduction
Sciatica is a condition where the pain radiates from the lower back down to the leg. This pain may go down the back, laterally, or anteriorly of the leg. It may affect unilateral or bilateral leg. Pain is severe in nature which affect patient physically as well as psychologically. According to acharya Charaka, gridharsi is one of the Vataja nanatmaja vikara1. Gridhrasi has been discussed in ayurveda by diffrent Acharyas under the heading of Vatavyadhi. ‘Sphikpurva katiprushto -rujanu janghapadam kramat
Grudhrasi stambhatodaihi grunhati spandate muhuhu’ ||2 ch. Chi 28/56\
Symptoms of Gridhrasi is Spikapurva i.e.pain starts at hip and radiates to Kati(waist), Prushta(back), Uru (thigh), Jaanu (knee joint), Janga (calf muscle), Paada(foot) along with pain there is other complaints like Stamba (stiffness), Ruka(pain), Toda(pricking type pain), Muhurspandana(tingling sensation), and if there is association of Vatakaphadosha then the symptoms like Tandra(lethargy), Gourava(heaviness) and Arochaka (anorexia) will be present.
The symptoms of Gridhrasi will closely resemble Sciatica and treatmet modalities told are basti, agnikarma,and siravedha3. As there is a major role of vata dosha, in ayurveda snehan and swedan are used as purvakarma of panchakarma as well as pradhankarma to treat various vatavyadhis. Snehan and swedan karma plays the important role in vatashamana. Jambeer Pinda sweda being one among the Swedana Karma (Sankar sweda) is a well known treatment for many Vatavyadhis including Gridhrasi4.
AIM AND OBJECTIVE
1. To study the role of Jambeer pinda sweda in gridhrasi w.s.r. to sciatica.
2. To study the Jambeer Pinda sweda in detail.
3. To study the Gridhrasi as per ayurveda texts.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
The study of different ayurvedic and modern literature has been done to fulfil the objective of the study. References regarding Jambeer pinda sweda are collected from various textbooks, previous work done, published research papers and detailed description regarding the types of sweda and its probable mode of action has been explained in the present study.
Nidana Abhighata (Trauma on lumbosacral spine), Atishrama (excessive exertion), Vishamacheshta (postural defects), Bharavahana (overloading), Aticheshta (abrupt unbalanced movements), Langhana (starvation), continuous jerky movements, sedentary lifestyle as well as psychological factors like Chinta, Shoka etc5.
Purvarupa In classics, the description regarding the Purvarupa of Gridhrasi is not available. Acharya Charaka opines that, in general the vague symptoms, or else any few symptoms of the respective Vatavyadhi in its minimal severity, that too in their initial stage are the Purvarupa. This nature of the Purvarupa is described as Avyakta Lakshana..Avyakta Lakshanas are Purvarupa of Vata Vyadhi (Ch. Chi. 28/19)6.
Rupa According to Charakacharya Gridrasi is Vataja Nanatmaja Vyadhi, it is of two types i.e Vataj and Vatakaphaja. The common lakshanas are pain starts from Sphika and then radiates towards Pada along with Stambha (stiffness), Toda (pricking pain), Spandana (twitching), and causes the Sakthiutkshepa Nigraha7 (restricted movements of lifting the leg); Whereas in Vatakaphaja type of Gridhrasi additionally Arochaka (anorexia), Tandra and Gaurava (heaviness) are found8.
Samprapti For the disease Gridhrasi, the detailed samprapti has not been mentioned in Ayurvedic classics. It is based on the Pratyaksha Lakshana found in the patients. Since Gridhrasi is a vatavyadhi, the general samprapti of vatavyadhi along with specific description available are considered here for the explanation of samprapti. Gridhrasi is Shoolapradhana vata vyadhi and Shoola cannot be produced without involvement of Vata Dosha. Vyana vayu and Apana vayu are especially vitiated. Gati (Prasarana, Akunchana, Utkshepana etc.) are the functions of Prakrita Vyana Vata. The hamperd Sakthi Utkshepa Karma indicates Vyana Dusti. Causes and Adhishthana of Gridhrasi resemble to Adhishthana and cause of Apana Dusti, hence Apana vitiation is prominent.
Gridhrasi is Vata prominent and Kapha Anubandhi Vyadhi, but independently kaphadosha cannot produce Gridhrasi. Acharya Sushruta mentioned that, in Gridhrasi, the vitiated Dosha affects the Kandara (ligaments) and thus, the manifestation. According to acharya Charaka Kandaras (ligaments) are the Upadhatu of Raktadhatu. and Kandara (ligaments) may also be taken as Sthula Snayu according to Chakrapani. Snayu is Mulsthana of Mamsa as well as updhatu of Meda. Hence, Rakta, Mamsa and Meda are taken as Dushya in the Gridhrasi. As Gridhrasi Nadi (sciatic nerve) is involved, so Majjadhatu may naturally also be involved. On the basis of Ashraya Ashrayi Bhava, with the vitiation of Vata and above mentioned Dushyas, their Strotas are also known to be involved. So, Rasawaha, Raktawaha, Mamsawaha, Medowaha, Asthiwaha and Majjawaha Strotas may be involved in this Vyadhi. The main Udbhavsthana of this Vyadhi is Pakwashaya because it is Nanatmaja Vatavyadhi. In the case of Vata Kaphaja Gridhrasi, amashaya may also be considered as an Udbhavsthana9.
Samprapti Ghataka
Dosha - Vata (especially Vyana) and Kapha10
Dushya - Rasa, Rakta, Mamsa, Meda, Asthi, Majja ,Sira, Kandara, Snayu
Ama - Jathragnijanya and Dhatwagnijanya
Agni- Jatharagni and Dhatwagni
Strotas- Rasavaha, Raktavaha, Mamsavaha, Medovaha, Asthivaha, Majjavaha
Strotodusti prakara- Strotosanga, Margavarodha
Rogamarga- Madyama
Udbhavasthana- Pakwashaya
Vyaktsthana- Sphik, Kati, Prusta, Uru, Jaanu, Jangha, Paada
Rogaswabhava - Chirakari
Sadhyasadyata - Yapya
Chikitsa Siddhant: While treating any disease, the first and foremost principle to be followed is to avoid nidanas (Su.U.1/25)11. For Gridhrasi, all the vataprakopaka hetus including external factors such as excessive walking, riding etc. should be avoided. Gridhrasi, being a vatavyadhi, the general line of treatment of vatavyadhies can applied to it.Acharya Charaka has advised dravyas having madhur, amla, lavana, snigdha, ushna properties and upakramas like snehana, swedana, asthapana and anuvasana basti, nasya, abhyanga, utsadana, parisheka etc (Ch. Su. 20/13)12. Snehanapurvak swedana is indicated in nirama vatavyadhies while only swedana is indicated in samavatavyadhies. Nadi, prastara, sankara etc. are the various types of sweda (Ch.Chi.28/78). Swedana liquifies the doshas and expands the srotasas, helping the doshas to travel towards their own sthana. Swedana activates agni, creates komalata, ruchi, clears srotasas, diminishes tandra (Su. Chi. 33/22) Snehanapurvak swedana relieves the symptoms such as harsha, toda, ruk, shotha, stambha, graha etc. It produces mruduta in the body. Charak says that proper snehan and swedana can make even dry wood flexible (Ch.Chi. 28/79-81)13. In Gridhrasi stambha, ruka, toda etc. are the main symptoms. Snehana and swedana by virtue of their vatashamak and dhatuposhak properties are useful in relieving the symptoms. Here ekanga sweda i.e. on the affected side only can be done.For Gridhrasi, Siravyadhana should be performed over the vein located between Khandara and Gulpha along with Basti and Agnikarma14. Difference between Chikitsa of Vataja and Vatakaphaja Gridhrasi.
Jambeer Pinda Sweda15
This is type of Sweda where Swedan is done by Potali containing Sliced Lemon and other ingredients.
According to different types of classifications, Jambeer pinda Sweda may be put under following groups:
- Agni bheda - Sagni Sweda
- Sthana bheda - Ekanga as well as Sarvanga Sweda
- Guna bheda - Snigdha Sweda
- Roga and Rogi bala - Madyama Sweda
- Charakokta Sankaradi bheda - Sankara Sweda (i.e.Snigdha Sankara Sweda)
- Vagbhatokta Tapadi bheda - Ushma Sweda
- Samshamana and Samshodhanangabhoota bheda - Samshamaniya Sweda
Procedure of Jambeer pinda Sweda:
Materials required16
1. Jambeer (chopped into pieces) - 750gms
2. Lashuna kalka- 60gms
3. Methika churna - 60gms
4. Haridra churna - 60gms
5. Shatapushpa churna -250gms
6. Cotton cloth - 4 (45 cm X 45cm)
7. Threads - QS
8. Vessels (For heating) - 2
9. Oil: Suitable oil
- For frying - 100ml (Mahanarayan Tail)
- For heating Pottalis - 200ml (Mahanarayan Tail)
- For Abhyanga - 100ml (Mahanarayan Tail)
- For Talam - 10ml ( Ksheerbala Tail)
10. Rasnadi Choorna - 5 to 8g
11. Soft Towels - 2
12. Attendant - 2
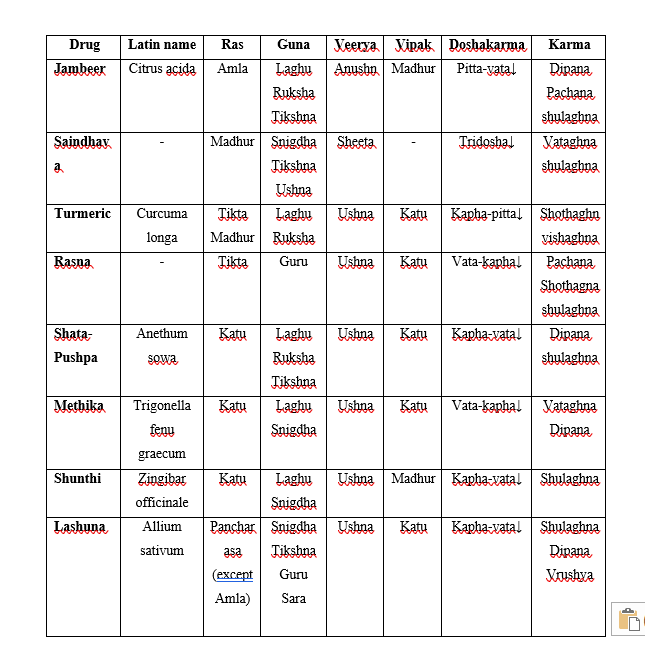
Different medicinal powders can be added, if necessary. Medicines used for Jambeer Pinda Sweda are-
Preparation of Pottali
The fresh Lemon should be washed in water and chopped into small pieces. The sliced lemon and other ingredients should be mixed thoroughly and fried together in 100 ml of appropriate oil till brown colour appears. Then divide it into four equal parts and made into Pottalis accordingly.
Procedure of Jambeer pinda Sweda:
Poorva Karma
The patient should be seated with legs extended over the Droni ( a specific table) facing to the East and abhyanga should be performed with prescribed medicated oil all over the body for about 10 minutes. Talam with suitable oil (10ml) / Choorna should be applied (Talam is a procedure of retaining medicines over the center of the head to protect body from temperature variations during the main treatment which is done before doing almost all Ayurvedic procedures).
Pradhana Karma
The prepared Pottalis should be heated with suitable oil by keeping on the hot iron pan. These pottalis are applied to the patients after checking the temperature throughout the body with mild pressure in seven prescribed positions by two attendants standing on both sides of the Droni. These pottalis are applied to the patient as per the general procedure for about 30-45 minutes. Care should be taken to maintain the temperature throughout the procedure by reheating the Pottalis.
Pashchata Karma
After the procedure, wipe off the body using clean dry towel and is covered with thin blanket for 10-15 minutes. Remove Talam and apply Rasnadi Choorna (5-8 gm). The patient should be advised to take complete rest for half an hour to one hour depending on disease and then take hot water bath.
Duration : 30-45 minutes
Precautions While preparing the medicines care should be taken to prevent charring and also while reheating the Pottalis.
- Tie the pottalis firmly to avoid leaking of the contents during the procedure.
- Every time the attendant should ensure the temperature of the Pottali by placing it over their own dorsum of hand. Also enquire the patient whether the temperature is bearable.
- If the patient feels any discomfort at any time during the treatment, the therapy should be stopped.
- Ideal time to perform the procedure is between 7-11 am and 3-6 pm.
Complications:
Burns and fainting:
If burns or fainting occurs, stop the Jambeer pinda sweda and Agnidagdha Chikitsa has to be done.
Mode of action of Jambeer Pinda Sweda in Gridhrasi:
The drugs used in Jambeer Pinda Sweda are having gunas like Ushnatwa and Snigdhatwa so it does Strotoshuddhi and Amapachana. Jambeer pinda sweda relieves stiffness by acting as Stambhaghna, Gauravaghna and also relieve heaviness in the body through sweating. The contents used are Sheetaghna by their Ushna quality and Swedakaraka as they promote sweating through which impurities of the body comes out.
Swedana increases the metabolic rate in the body. Ushna Guna of Sweda causes vasodilatation, thus it increases blood circulation. Swedana enhances the elimination of waste products and more absorption of Sneha or drugs through the twacha(skin), as in Jambeer Pinda Sweda we use Vata-Kaphahara drugs when they are absorbed into the body they does their action along with Swedana. Also it stimulates muscles and nerves, which promotes renovation of muscles and nerves17.
The probable mode of action of Jambeer pinda sweda in Gridhrasi can be explained under following headings:
Thermal effect
According to Kligman, diffusion through the skin is a temperature dependent process, so raising the skin temperature will enhance the transdermal delivery of various drugs by increasing skin permeability, body fluid circulation, blood vessel wall permeability, drug solubility. External heating will dilate the penetration pathways in the skin, increases kinetic energy and movement of particles in the treated area and facilitate drug absorption.
Heat is having indirect effect on-
- Muscle tissue - Increases the temperature of muscle tissues
- Muscle relaxation
- Increased activity of Sweat glands - Reflex stimulation of Sweat glands resulting from effect of heat on the sensory nerve endings.
Procedural effect
Procedure is exceedingly beneficial to the skin as it works directly on the lymphatic system. This system is supplementary to the blood vascular system and offers an alternative route for the return of tissue fluid to the blood stream. By stimulating lymphatic flow and generating heat through friction (rubbing) and application of the oils, massage cleanses and vitalizes the body without causing the build-up of toxins. Thus procedure quickens the circulation of blood and lymph and dislodges the toxins and increases the vitality of the tissues.
Drug effect
The drugs used for the Jambeer Pinda Sweda are having Vatahara and Kaphahara property and all the drugs used here have Ushna Veerya, Snigdha, Sukshma Guna. Thus the drugs act on the Vata directly.
mode of action
Discussion
The main and direct reference available on the mode of action of Bahirparimarjana is from Sushruta Samhita (Su.Sha.9/9)18 and Charaka Samhita (Ch.Su.11)19. Charkacharya says that the therapy which by external contact through abhyanga (massage), Sweda (fomentation), pradeha (pasting), parisheka (sprinkling), unmardana (pressing) etc. removes disorders. It explains that “The branch of body’s peripheral conduction network with their portals in the skin is concerned with perspiration, perception of cutaneous pleasure and pain sensations, as well as circulation of tissue fluid. Conduction of the activity or potency of the therapeutic regimen or agent into the body, after conversion (transduction) in the skin, also forms their attribute”.
Swedana is a karma where stimulating the body temperature by contact with the external heat source, there by producing Sweda. The Ushna Guna of Swedana Karma stimulates the sympathetic nervous system and produces vasodilatation. It also increases the circulation of Rasa and Rakta dhatu in the body. Due to Swedana karma, the Leena Dosha are liquefied and come out through micropores over the skin, resulting in more excretion of liquefied vitiated Dosha from body.
Action of Jambeer pinda Sweda on specific symptoms of Gridrasi:
Effect on Ruka-
Ruka i.e. pain is due to Vatavridhi. Once Vata vitiation is corrected Ruka will be reduced. As the drugs used are having Ushnavirya, Vatakaphahara, Vedanasthapaka and Shothahara property helps in reducing the pain. Also by increasing temperature locally to the muscle, improves blood circulation and helps to reduce pain.
Effect on Stambha-
Stambha is the result of Kapha or Ama.The drugs used in Jambeer Pind sweda are having Ushna, Tikshna and Sukshma Gunas which helps to reduce Kapha and Ama and hence reduces stambha.
Effect on Toda-
During procedure the drugs used in general relieve muscle spasm and thus relieves pressure on the nerves, then blood supply to the nerves is improved and thus relieves pain.
Effect on Spandana-
Spandana or pulsating pain occurs as a result of Vataprakopa. Due to Swedana karma, Vataprakopa is reduced by Snigdha and Ushna Guna of Dravyas used, leading to reduction in Spandana.
Effect on Arochaka-
Increased body temperature increases sympathetic activities, releasing hormones like epinephrine, norepinephrine, cortisol and thyroid hormones. It accelerates metabolic rate and stimulates process of lipolysis, thereby increasing demand of oxygen and increased output of wastes i.e. digestion of Ama leading to Agni Dipana.
Effect on Gourava-
Gourava is due to Aapa and Prithvi Mahabhoota. During procedure, Aapa Mahabhoota is coming out as perspiration leading to reduction in Gourava and brings Laghava in the body.
Conclusion
Gridhrasi is one of the Nanatmaja Vata Vyadhi, intervening with the functional ability of Kati (lower back) and Pada (lower limbs). In Gridhrasi, onset of Ruka, Toda and Stambha is initially in Kati and radiates distal to Prushtha, Janu, Jangha till Pada. This is the unique feature of the Gridhrasi. Snehana, Swedana and Mrudu Sodhana are the Principles of Chikitsa in all Vatavyadhi. Agnikarma and Siravyadha are mentioned among the lines of treatment, as Snayu and Kandara are involved as Dushya. Shamanoushadhis are also mentioned by many Acharyas, along with this an added advantage will be achieved if Snehana and Swedana are done which relieves Stambha, Gaurava, Sheetata and Ruka. According to Charaka Samhita, Sankara Sweda is one among 13 types of Sagni Sweda A prepared pottali of fresh drugs is heated to lukewarm and applied over the painful parts. It is an ideal treatment for application of heat to specific part of body. Due to direct contact of heat the penetration is deeper and hence effectively reduces pain, swelling and stiffness. This is unique and effective method of managing severe pain in Gridhrasi i.e. Sciatica.
References
Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Sutrasthana adhyaya 20, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.113, Shloka no.11.
2. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Chikitsasthana adhyaya 28, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.619, Shloka no.56.
3. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Chikitsasthana adhyaya 28, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.621, Shloka no.101.
4. Pt. Harishastri Bhishagacharya, Ashtang Hridaya, Arundatta and Hemadri Tika, Sutrasthana adhyaya 13, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.211, Shloka no.1.
5. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Chikitsasthana adhyaya 28, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2019, Page no.617, Shloka no.15-18.
6. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Chikitsasthana adhyaya 28, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.617, Shloka no.19.
7. Kaviraj Aambikadatta Shastri. Susrutha Samhita, tattvasandipika hindi commentary, Nidansthana adhyaya 1, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2015, Page no.303, Shloka no.74.
8. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Chikitsasthana adhyaya 28, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2019, Page no.619, Shloka no.56-57.
9. Brijesh R Mishra, Shweta G Nimkarde, Abhishek B Mishra, Management of Gridrasi with Agnikarma and Raktamokshana: A Review at ayurline; IJ-RIM 2019;3(1): 1-5.
10. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Chikitsasthana adhyaya 28, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.619, Shloka no.57.
11. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Sushrut Samhita, Nibandhasangraha tika, Uttartantra adhyaya 01, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2014, Page no.597, Shloka no.25.
12. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Sutrasthana adhyaya 20, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.114, Shloka no.13.
13. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Chikitsasthana adhyaya 28, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.620, Shloka no.79-81.
14. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Chikitsasthana adhyaya 28, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2019, Page no.621, Shloka no.101.
15. Dr.Vasant C Patil, Principles and practice of panchakarma, chapter 9, Swedana karma, Chaukhambha Publications, New Delhi, Reprint 2018, Page no.214.
16. Pavitra, Shaila Borannavar, Ananta Desai, Role of patrapinda sweda in Gridrasi w s r to sciatica: A Review Article at JAIMS 2020; Page No. 3-4.
https://jaims.in/jaims/article/view/1058
17 Dr.Vasant C Patil, Principles and Practice of Panchakarma, chapter 9, Swedana Karma, Chaukhambha Publications New Delhi, Reprint 2018,pn 247.
18. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Sushrut Samhita, Nibandhasangraha tika, Sharirsthana adhyaya 09, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2014, Page no.385, Shloka no.9.
19. Vaidya. Yadavji Trikamji Acharya, Charaka Samhita, Chakrapanidatta tika, Sutrasthana adhyaya 11, Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, Reprint 2017, Page no.78, Shloka no.55.
