Case Report
Year: 2022 |Volume: 1 | Issue: 03 |Pages: 178-184
Exploratory Laparotomy in Huge Left Mucinous Cystadenoma- A Single Case Study
About Author
Correspondence Address:
Dr Anjali Suryawanshi, PG Scholar, Department of Shalyatantra, Shri Ayurved Mahavidyalaya, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India. Email: anjalisuryawanshi8394@gmailcom. Mobile No-7743842877
Date of Acceptance: 2022-09-30
Date of Publication:2022-10-16
Article-ID:AYU_31_10_22 https://ayuscript.com
Source of Support: Nill
Conflict of Interest: Nill
How To Cite This Article: Suryawanshi A, Shinde J, Khobragade S, Exploratory Laparotomy in Huge Left Mucinous Cystadenoma- A Single Case Study. AYUSCRIPT 2022;1(3):178-184
Abstract
Introduction: Ovarian cyst is most common problems in women due to changing life style, food habits. Ovarian cyst is closed, sac like structure within the ovary that are filled with a liquid or semi-solid substance. Mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary is at the benign end of the spectrum of mucin-containing epithelial ovarian tumors.
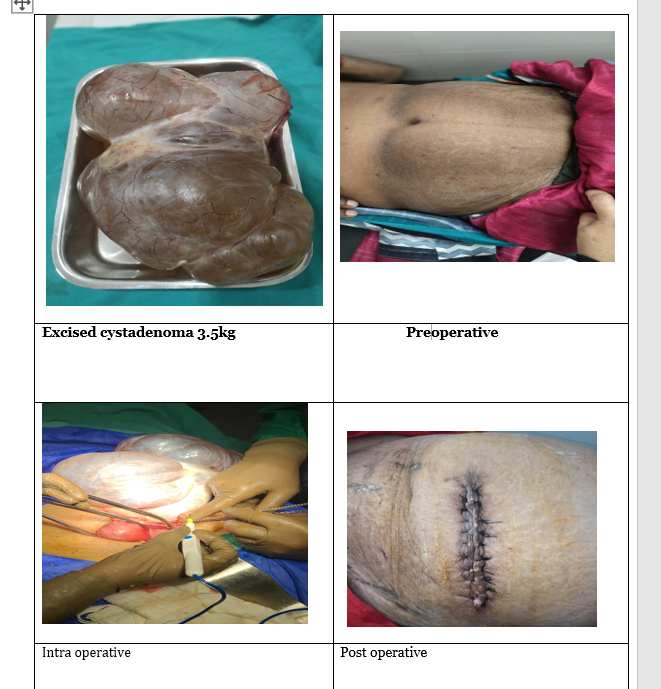
Method: This case study deals with post- menopausal 70-year lady having chief complaints with a large cystic swelling at all over abdomen and mild pain at lower abdomen, heaviness in abdomen with nausea since 1 year. After local examination, USG and CT scan reports, provisional diagnosis was made as ovarian Cystadenoma and decided to do exploratory laparotomy. During intra-operative procedure large cyst was noted arising from left ovary with multiple cysts filled with clear fluid in one section. The cyst of 3.7 kg was excised by laparotomy.
Result: A left mucinous cystadenoma was successfully treated by surgical procedure. The patient tolerated the surgery well and recovered without complication. After operation, she returned to her normal activity. No any recurrence was noted during the follow up up to 3 months after surgery.
Conclusion: Differential diagnosis of large mucinous cystadenoma can be mesenteric cyst or hydatid cyst. Conservative management of cystadenoma is depending on the following factors like symptoms, size of cyst, age of patient and menopausal condition of patient hence, exploratory laparotomy is choice of surgery among all surgical advancements for huge mucinous cystadenoma.
Keywords: ovarian cyst, exploratory laparotomy, mucinous cystadenoma.
Introduction
Mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary is at the benign end of the spectrum of mucin-containing epithelial ovarian tumors.1 Ovarian cystadenoma is benign tumor that arising surface epithelium of the ovary. It is most common type of epithelial ovarian tumor accounting for approximately 15% of this neoplasia. About 80% of mucinous tumors are benign, 10% are border line and 10% are malignant2.The merger of mucinous cystadenomas with dermoid cyst indicates that some are germ cell origin.
Now a days women’s life, ovarian tumors can present at any age. Ovarian cyst is most common condition in females due to various types of hormonal changes. Ovarian cyst are closed, sac like structure within the ovary that are fills with a liquid or semi-solid substances.3 Mostly Ovarian cysts are more common in young female patients of child bearing age as noted in recently and are rare before puberty or after menopause. the condition is less common after menopause.4 sometime Small ovarian cyst may not cause signs and symptoms. Few large cysts are more likely to cause signs and symptoms while huge cyst causes symptoms of other systems.5 After local examination like palpable lower abdominal swelling and mild pain in lower abdomen especially in huge cyst. Diagnosis is confirmed by USG and CT or MRI abdomen which revel the size, site and contents in the cyst. Serum CA-125 assay is a useful tool that helps to distinguish between benign and malignant ovarian masses. The combination of normal findings at serum CA-125 assay, imaging, and clinical findings exclude the possibility of ovarian cancer.6The management of ovarian cyst depends upon age of the patients as well as size of cyst7The huge size of ovarian cyst causes pressure on pelvic anatomy which causes pressure symptoms of gastro-intestinal and urinary tract.8Laparoscopy is considered the gold standard approach to accomplish benign ovarian cysts. The benefits of laparoscopy include reduced postoperative analgesic requirement, earlier mobilization, cosmetic advantages, earlier discharge from the hospital, and return to normal activity. A major factor that will make to perform laparotomy is the size of the ovarian mass.
Case study: A 70 years female, married since 50years with menopause since 10years came to our institute on 14 dec 2021. The patient was having chief complaints of gradually increasing abdominal size for since 1 year. The abdominal swelling accompanied with dull pain all over abdomen. She also complained with nausea and giddiness. She was having sensation of fullness and heaviness in abdomen for since one year with loss of appetite. Obstetric history G1P1L1A0D0. Previous USG report suggested that huge cystic mass lesion in pelvis and abdomen? mucinous cystadenoma of ovary. Due to her socio-economic status, she couldn't get operated. When she started pain in all over abdomen, increasing abdominal swelling and loss of appetite her son brought her to our hospital for further management. No specific drug history was noted by patient. Local examination revealed abdominal distension with 95cm abdominal girth. On palpation huge cystic mass extending from lower abdomen to Xiphi-sternum was palpable. The cystic mass was mobile perpendicular to the long axis of mesentery and its consistency was soft with presence of fluid thrill. On general examination, she was thin built and undernourished. Her Wight was 65 kilograms and physical examination revealed vital functions were stable and lab investigations were normal.
(Table-1)
|
Investigation |
Observed value |
Normal value |
|
Hb%- |
12.7 |
14-16 |
|
RBS |
96 MG\DL |
<=140 mg% |
|
HIV |
- ve |
|
|
HbsAg |
-ve |
|
|
Ca 125 |
47U\ml |
0-35 |
|
PT(INR) |
1.03 |
0.8-1.2 |
|
creatinine |
0.89 mg% |
0.80-1.40mg% |
Result: A left mucinous cystadenoma was successfully treated by surgical procedure. The patient tolerated the surgery well and recovered without complication. After operation, she returned to her normal activity. No any recurrence was noted during the follow up up to 3 months after surgery.
MRI REPORT: Large Well Defined Multiloculated Cystic Lesion with Internal Septation Seen Within Abdominopelvic Region Possibility of Cystic Ovarian Neoplasm? Cystadenoma.
PRE OPRATIVE-PROCEDURE: Informed and written consent
Inj.T.T 0.5 ml
Bupivacaine sensitivity test done.
Part preparation done.
Operative procedure: - Under spinal anesthesia midline incision was taken from xiphi-sternum to 4cm above pubic-symphysis. A large cystic mass extending from splenic flexor of colon to pelvis covering almost all the abdominal cavity was seen. All intestines were shifted to Morrison pouch. Tumor bound to be adherent with fimbriae and broad ligament of uterus with non-visible ovary. It was diagnosed as left ovarian cyst. Cyst excised with ligation of broad ligament, fimbriae and fallopian tube. Cyst was multiloculate with clear fluid in one section. CT scan. Abdominal cavity checked for any other pathology.
img
Discussion
Mucinous cystadenomas have a smooth surface and are usually multilocular and sometimes unilocular. They range in size from a few centimeters to greater than 30 cm with a mean of 10 mucinous cystadenoma is composed of multiple cysts and glands lined by simple non-stratified mucinous epithelium resembling gastric foveolar-type or intestinal epithelium containing goblet cells and sometimes neuroendocrine cells or Paneth cells9. Ovarian neoplasms may be divided according to original cell types into three main groups: epithelial, stromal, and germ cell. Out of these groups, the epithelial tumors are most common type. The most common benign ovarian neoplasm is the benign cystic teratoma; however, according to some studies, it is mucinous cystadenoma. Ovarian mucinous cystadenoma is a benign tumor that arises from the totipotent surface epithelium of the ovary. The association of mucinous cystadenomas with dermoid cysts indicates that some are of germ cell origin and an association with Brenner tumors implies a surface epithelial origin for another subset10.It is a multi-locular cyst with smooth outer and inner surfaces. It tends to be huge in size. On cut section, the content inside is thick, viscid, mucin-a glycoprotein11. As with all ovarian tumors, staging is surgical. However, mucinous tumors of the ovary are distinct from other epithelial ovarian tumors in that they are more likely than serous carcinomas to manifest at an early stage. Eighty-three percent of mucinous ovarian carcinomas are FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics) stage I at presentation, in contrast to 4% of serous carcinomas12. In Many cases, cysts are treated by surgery via laparoscopy or laparotomy cyst excision or cystectomy with Oophorectomy13. The choice between laparoscopy and laparotomy, conservative or radical treatments may be difficult and depends on the patient’s age, the size of the cyst. A major factor that makes the surgeon decide to perform laparotomy.
Conclusion
Diagnosis is often delayed because women frequently fail to report symptoms or attribute them to other causes (eg, menopause). This patient thought she was "getting fat" and ignored her symptoms until the tumor had grown significantly. Fortunately, malignancy did not develop during the 5-month gap between the first symptoms and diagnosis. Differential diagnosis of large mucinous cystadenoma can be mesenteric cyst or hydatid cyst. Conservative management of cystadenoma is depending on the following factors like symptoms, size of cyst, age of patient and menopausal condition of patient14 Hence, exploratory laparotomy is choice of surgery among all surgical advancements for huge mucinous cystadenoma.
References
1. Thomassin-naggara I, Bazot M, Daraï E et-al. Epithelial ovarian tumors: value of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and correlation with tumor angiogenesis. Radiology. 2008;248 (1): 148-59. doi:10.1148/radiol.2481071120 - Pubmed citation
2.Prat J, D’Angelo E, Espinosa I. Ovarian carcinomas: at least five different diseases with distinct histological features and molecular genetics. Hum Pathol 2018; 80:11–27. Crossref, Medline, Google Schola
3.Datta D. C. D C Datta’s Text book of Gynaecology including contraception; Edited by HiralalKonar;sixth edition 2013; page no. 276-89.
4.Datta D. C. D C Datta’s Text book ofObstetrics including perinatology and contraception; Edited by HiralalKonar; seventh edition 2013; p- 310.
5.Agrawal SP, Rath SK, Aher GS, Gawali UG. Large ovarian tumour: A case
Report.Int J Sci Stud 2015; 3(3): 143-145
6.Jeong YY, Outwater EK, Kang HK. Imaging evaluation of ovarian masses. Radiographics. 2000 Sep-Oct;20(5):1445-70. [PubMed]
7.Datta’s Text book of Obstetrics including perinatology and contraception; Edited by HiralalKonar;seventh edition 2013; p- 310. 12010; 8:24
9. Ovarian Cystadenoma Faten Limaiem; Manidhar Reddy Lekkala; Mouna Mlika.Last Update: April 30, 2022.
10 Seidman JD, Khedmati F. Exploring the histogenesis of ovarian mucinous and transitional cell (Brenner) neoplasms and their relationship with Walthard cell nests: a study of 120 tumors. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008 Nov;132(11):1753-60. [PubMed]
11.Datta D. C. D C Datta’s Text book of Gynecology including contraception Edited by Hiralal Konar; sixth edition 2013; p- 279
12. Seidman JD, Horkayne-Szakaly I, Haiba M, Boice CR, Kurman RJ, Ronnett BM. The histologic type and stage distribution of ovarian carcinomas of surface epithelial origin. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23(1):41–44. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
13.Nwobodo EI. Giant mucinous cystadenoma: case report. Niger J ClinPract. 2010; 13(2):228-9
14.Gonzalez DO, Minneci PC, Deans KJ. Management of benign ovarian lesions in girls: a trend toward fewer oophorectomies. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Oct;29(5):289-294
